Computer Modeled Structural Analysis
Structural analysis is a branch of solid mechanics which uses simplified models for solids like bars, beams and shells for engineering decision making. Its main objective is to determine the effect of loads on the physical structures and their components. In contrast to theory of elasticity, the models used in structure analysis are often differential equations in one spatial variable. Structures subject to this type of analysis include all that must withstand loads, such as buildings, bridges, aircraft and ships.
Structural analysis uses ideas from applied mechanics, materials science and applied mathematics to compute a structure’s deformations, internal forces, stresses, support reactions, velocity, accelerations, and stability. The results of the analysis are used to verify a structure’s fitness for use, often precluding physical tests. Structural analysis is thus a key part of the engineering design of structures.
Computer modeled structural analysis has become more available and better refined in recent years. It allows rapid answers to complex questions.
Making the Complicated Simple
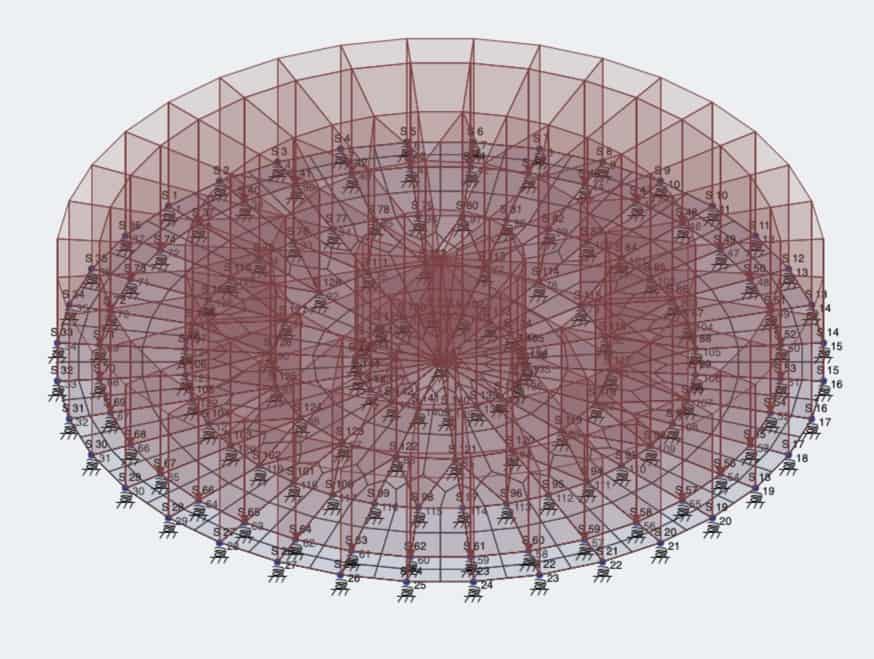
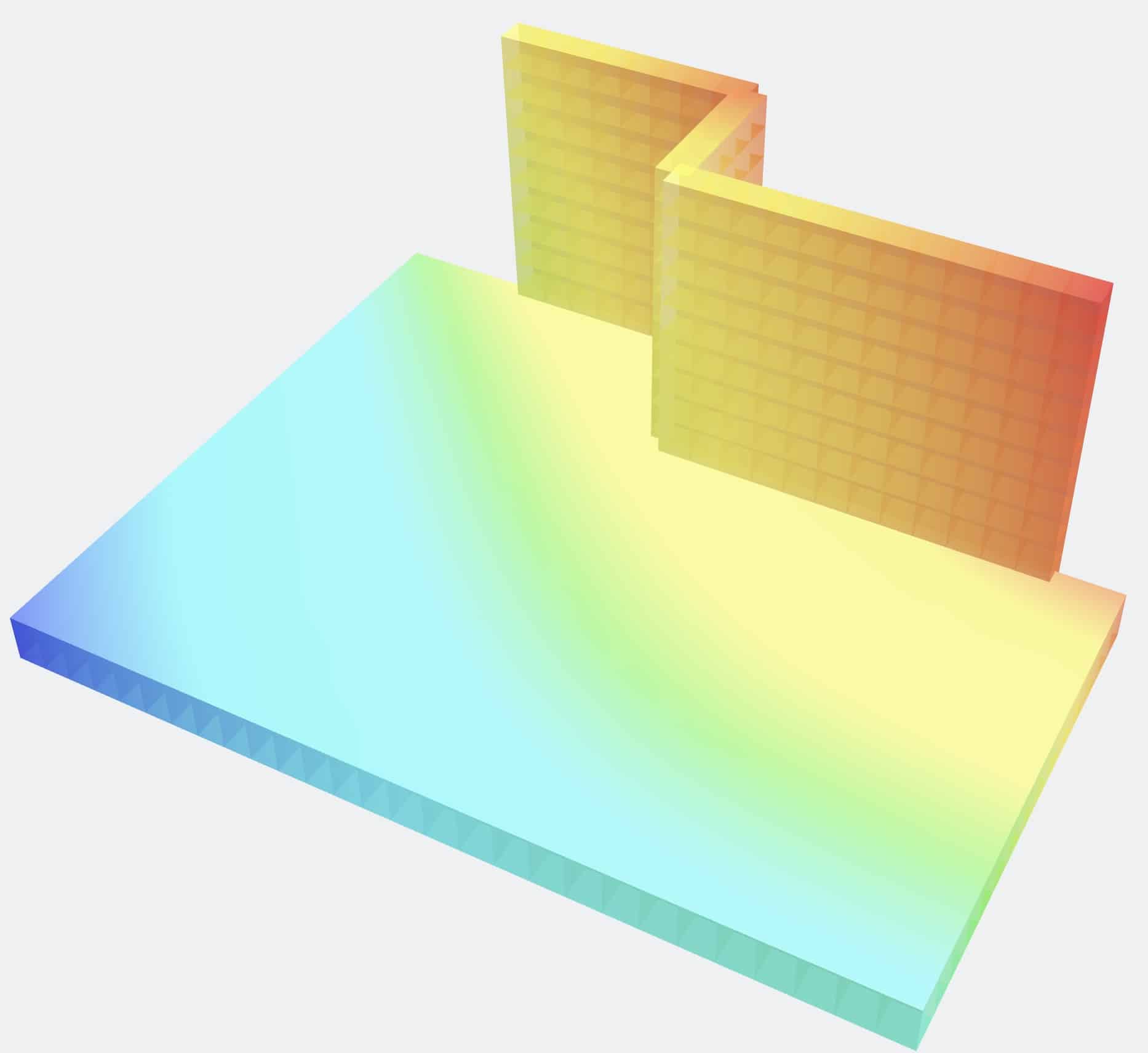
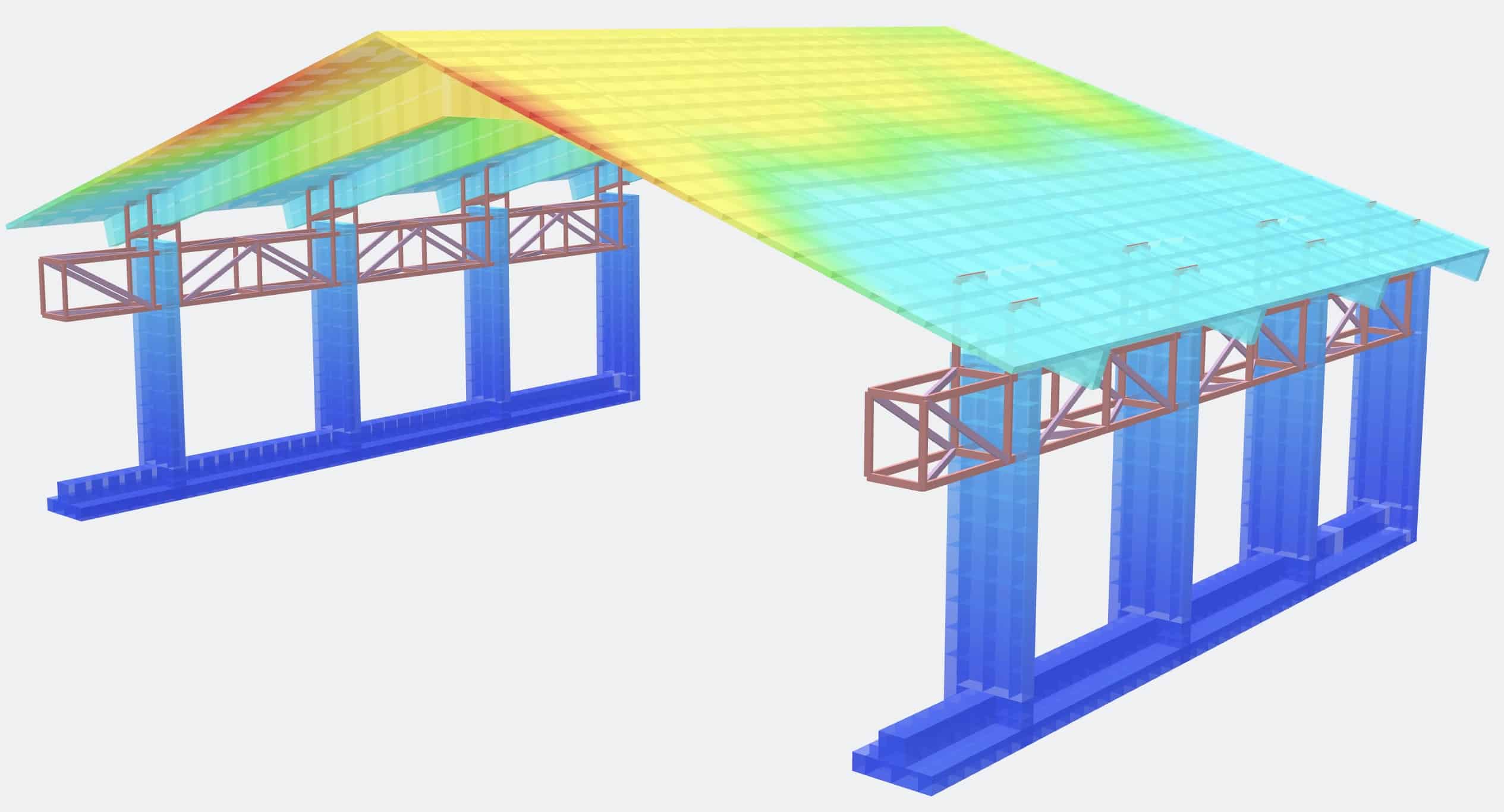
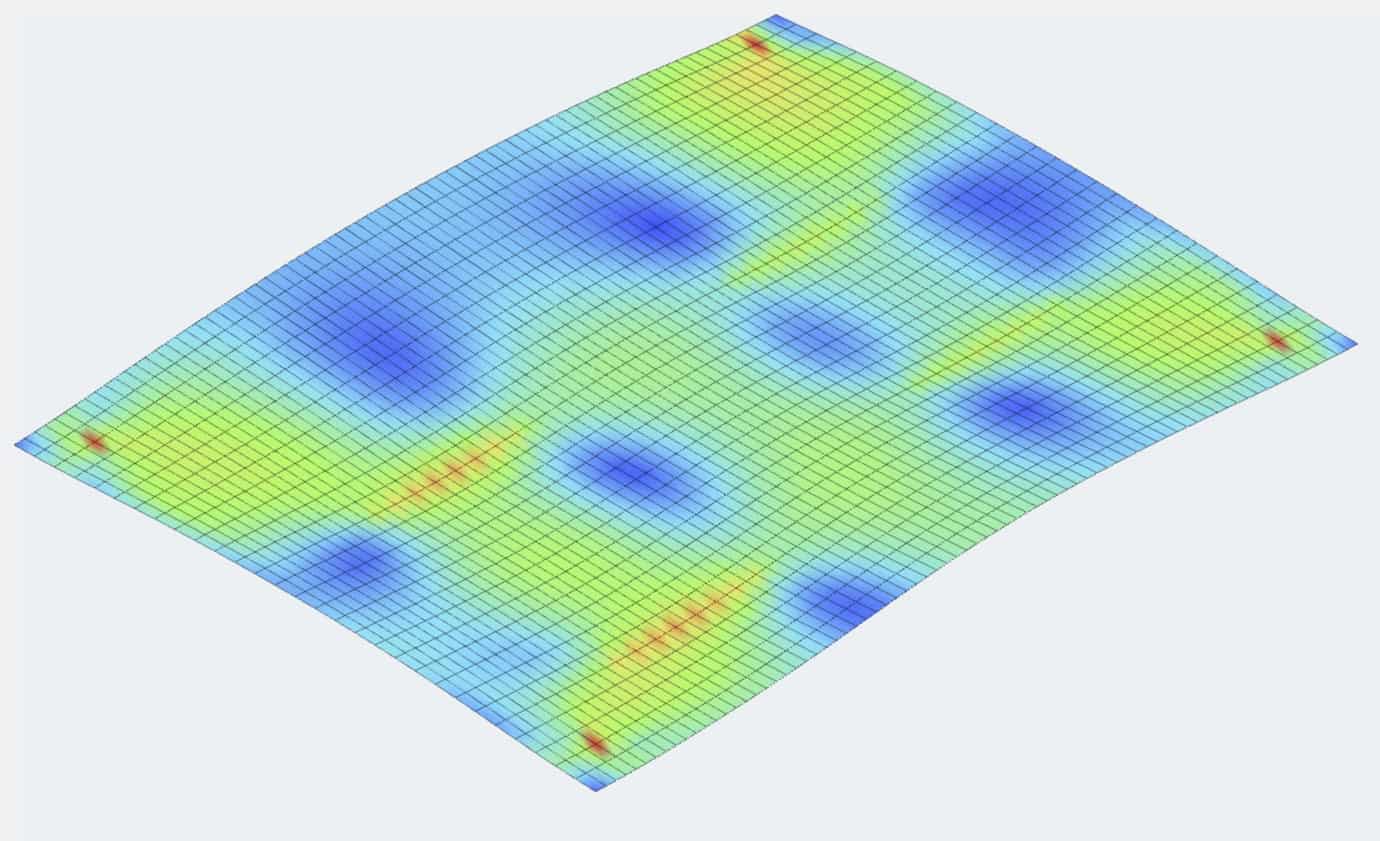
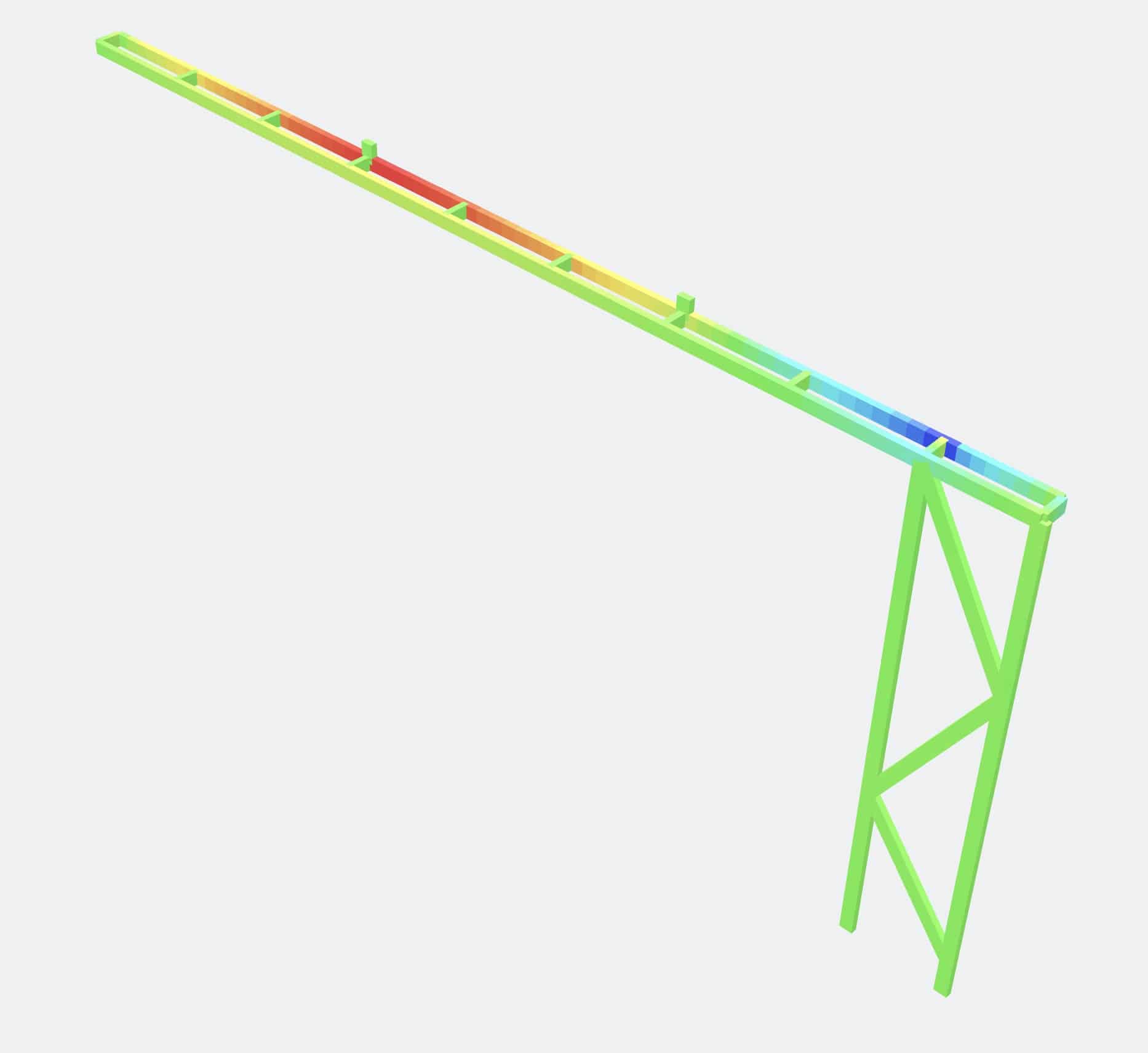
Computer modeling requires defining the structure with X, Y, and Z coordinates and fitting the various components between these coordinates. Components can be beams, columns, walls, floors, or roofs. The components can be supported by fixed foundations, sliding foundations, or foundations that act as springs. Loads include self-weight, building code specified loadings, and endless other possibilities.
Some examples of these computer modeled analyses can be seen below.

Vacek LLC, formerly Vacek Group, is a Houston area structural and architectural engineering company established in 1994. The company offers years of experience to insurance companies, attorneys, architects and the private sector.

NAVIGATION